How Pasteurizers Fit into Industrial Gelato Manufacturing Workflows
In commercial gelato production, pasteurization is not simply a food safety step—it is a core process that directly affects product quality, production efficiency, and workflow stability. Unlike household or retail dairy processing, gelato factories rely on controlled pasteurization to ensure consistency across large production volumes.
This article explains how the pasteurization process works within a commercial gelato production line, and why proper integration of pasteurizers is critical for professional gelato manufacturing.
The Role of Pasteurization in Gelato Production
Pasteurization in gelato production serves three primary functions:
-
Ensuring microbiological safety of the gelato mix
-
Stabilizing the mix structure for consistent freezing
-
Preparing the mix for aging and batch freezing
In factory environments, pasteurization must be repeatable, scalable, and synchronized with downstream equipment such as batch freezers and aging tanks.
Typical Pasteurization Workflow in a Gelato Production Line
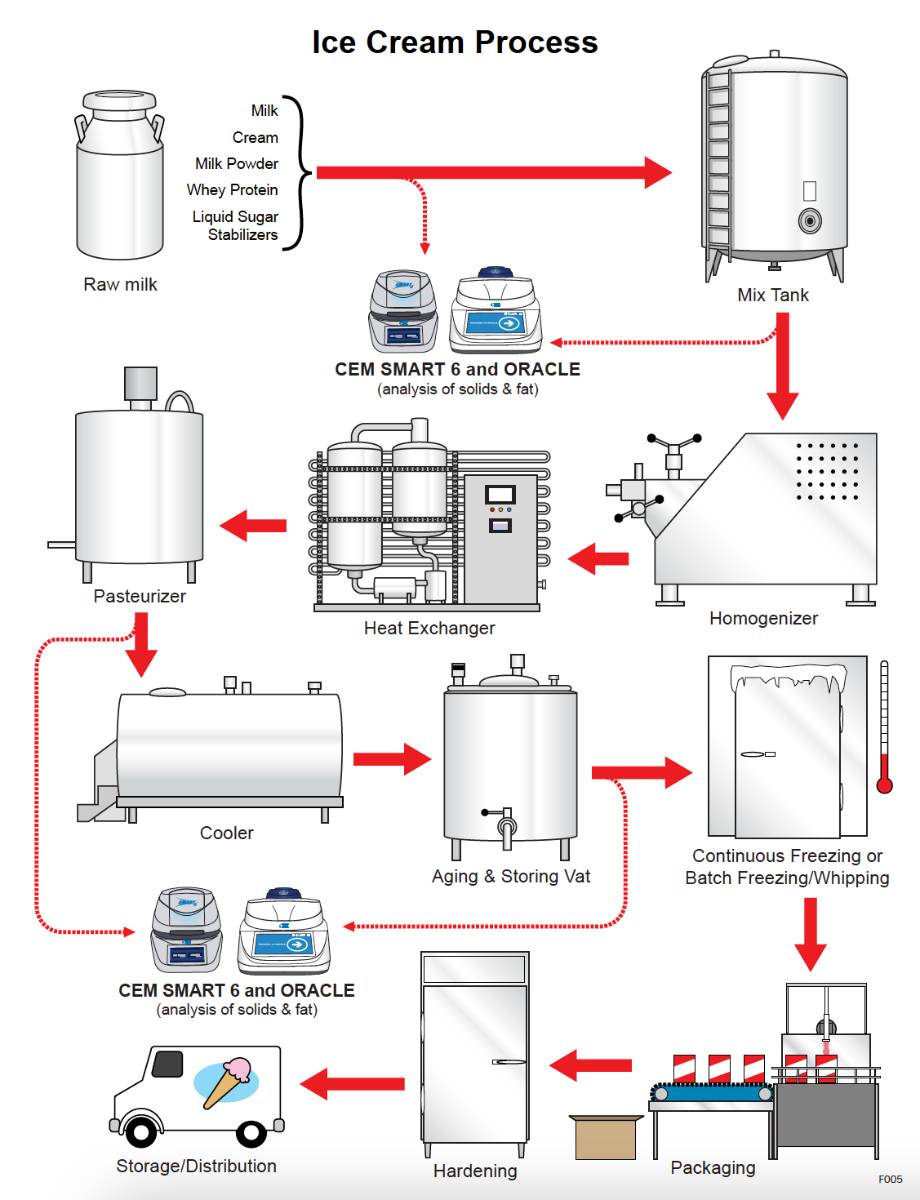
A standard commercial gelato production line follows this sequence:
-
Ingredient mixing
-
Pasteurization
-
Rapid cooling
-
Aging (maturation)
-
Batch freezing
-
Storage or display
Pasteurizers act as the central control point between raw ingredients and finished gelato structure.
Pasteurization Temperature and Holding Logic for Gelato Mix
Unlike generic dairy processing, gelato mix requires precise temperature control to preserve flavor balance and texture.
Key considerations include:
-
Heating the mix to pasteurization temperature without protein damage
-
Maintaining a controlled holding time to ensure safety
-
Rapid cooling to prevent bacterial regrowth
Commercial pasteurizers are designed to maintain these parameters consistently across repeated cycles.
Batch Pasteurization vs Continuous Processing in Gelato Factories
Most gelato factories use batch pasteurization rather than continuous systems.
Batch pasteurizers allow:
-
Better control over individual recipes
-
Easier flavor changes
-
Higher flexibility for artisan and semi-industrial production
Continuous pasteurization is more common in large-scale dairy operations but is less suited to the frequent recipe changes typical in gelato production.
Coordination Between Pasteurizers and Batch Freezers

For efficient production, pasteurizer capacity must align with batch freezer throughput.
Best practices include:
-
One pasteurization batch supplying one to two batch freezer cycles
-
Avoiding idle time caused by mismatched capacities
-
Scheduling pasteurization cycles to match freezing demand
Poor coordination can create bottlenecks and reduce overall factory efficiency.
Pasteurization and Aging: Preparing the Mix for Freezing
After pasteurization, gelato mix is typically aged under controlled conditions. This aging phase allows:
-
Fat crystallization
-
Protein hydration
-
Improved texture stability
Pasteurizers that integrate effectively with aging tanks help ensure consistent gelato quality.
Why Pasteurization Process Design Matters in Gelato Factories
In commercial environments, pasteurization affects more than safety:
-
Product consistency across batches
-
Energy efficiency
-
Labor scheduling
-
Scalability for future expansion
Well-designed pasteurization processes reduce waste, improve repeatability, and support long-term production planning.
Summary: Pasteurization as a Core Process in Gelato Manufacturing
In a commercial gelato production line, pasteurization is a strategic process, not a standalone step. Proper integration of pasteurizers ensures food safety, supports texture development, and enables efficient factory workflows.
Understanding how pasteurization fits into the overall production line helps gelato manufacturers design systems that deliver consistent quality and scalable performance.




